Installation Improvements Project - 0.1.3¶
Status: In progress Review status: Approved
Team¶
| Role | Assignee | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Owner | Mukesh | |
| Backend Helpers | Dominykas | |
| Frontend Helpers | Rajat | |
| Design Helper | Ghislaine | |
| Design Reviewer | Kriti | |
| Backend Reviewer | Brent | |
| Frontend Reviewer | Pavish | |
| Contributors (future work discussions) | Brent, Kriti, Mukesh, Pavish | Anyone else interested can join |
Problem¶
The current problems we face in our installation process and documentation are:
- We’re targeting too many different use cases for Mathesar in our current documentation, and we need to simplify things.
- Installing Mathesar involves many steps, which makes the process brittle and introduces failure points that we can avoid.
- There is too much configuration needed before Mathesar can be started, which makes it difficult to try Mathesar out quickly.
- Configuration is done through scripts specific to certain installation mathods, and not in the product itself, which makes some installation methods much more difficult and inconsistent.
- This also makes the documentation harder to maintain since each installation method has very different steps.
See also: Diagram of existing steps involved in installation
Based on previous discussions, we’d like to prioritize the following “user personas”:
- Someone trying Mathesar out quickly (and can use Docker)
- Someone installing Mathesar on a PaaS
- Someone installing server & DB on same remote system
- Someone installing server & DB on separate remote systems
We haven’t finished talking about the solutions for these personas, but during the conversations we’ve had, we’ve identified some low hanging fruit that can improve our current installation process.
This project involves fixing those low hanging fruit and finishing the discussions for prioritizing solutions we want to work on in the future.
Outcome¶
- The number of steps involved in installing and starting Mathesar will be reduced
- Some steps involved in setting up Mathesar will be moved to the UI so that they will be the same across all the installation methods. It also has the benefit of reducing the steps involved before starting Mathesar instead of having the user fiddle around with some command.
- We will have a clear technical plan and priority list for what we’ll implement to simplify installation in future cycles.
Solution¶
The low hanging fruit we plan to tackle in this cycle:
- Move superuser creation to the UI
- Problem solved: configuration moved to product instead of outside scripting
- Build single Docker image containing both Mathesar and Postgres
- Problem solved: simplifies the process of trying Mathesar out quickly, reduces overall configuration
- Create Mathesar Debian package
- Problem solved: Reduces installation steps (dependencies, static file building, etc.). We’re choosing Debian because it’s the most common server.
- Update documentation to provide non-superuser permissions while installing Mathesar
- We’re prioritizing this because it’s a user reported issue and has been brought up in launch user feedback.
Issues we need to resolve through discussions:
- Configuration values like the secret key should be generated automatically. Other configuration options like adding a user database credential should be moved to the Mathesar UI. We are currently blocked by discussions for storing configuration values and we will be having meetings in this cycle to figure out a plan which can be implemented in later cycles
- Problem solved: Removes configuration steps needed for starting Mathesar
- Research and decide on which PaaS to support
- Problem solved: Reduces installation steps and benefits someone looking to try Mathesar quickly
- Finalize technical plan and priorities for making installation easier for all the targeted personas
Overview diagram showcasing the relation between the problems, solutions and the outcome
Stretch goals¶
Most of these solutions will be useful for laying the ground work for future work and won’t necessarily be complete by the end of the cycle (they might not added to the documentation). These are lower impact because they focus more on “medium” priority personas.
- Build helm charts
- Limitations: Just the yaml file for the mathesar app. We won’t be adding to the installation documentation or adding it to the helm repo in this cycle
- Problem solved: Reduces steps for Kubernetes user and also requested by users
- Build zipapps
- Limitations: Just the script to generate the zipapp. It won’t be added to the installation documentation in this cycle
- Problem solved: Reduces steps for non-docker and non-debian installs
- Support SQLite as an additional datasource for the internal database
- Limitations: Only the codebase refactor necessary to support SQLite. Documenting the configuration option will be done in later cycle
- Problem solved: Makes it easier to start Mathesar for users using a install package without inbuilt Postgres server package
- Build static files and upload it to the release page
- Problem solved: Makes it easier to install Mathesar for users not using the Debian package or if they want to serve static files from a different server.
- This is a low priority because most of the installation methods documented make use of pre-built packages which comes with static files packaged with them and are much easier to use
- Move documentation on auxiliary services (Caddy, Watchtower) to different docs (will be called as best practice guide)
- Problem solved: Makes our documentation easier to maintain.
- This is a low priority as it does not improve experience instead makes the documentation more cleaner and more focused.
Meetings¶
- We will be having meeting every week to discuss further improvements to our Installation process.
- Kriti and Mukesh will meet every week to plan ahead of the meetings.
- The meeting topics are not definitive and can change.
- Some of the topics to discuss
- Simplifying installation for Personas not covered by previous meetings
- PaaS offering to support
- The location and workflow for storing the configuration details
Timeline¶
| Date | Outcome | |-|-|-|-|-| | 2023-07-17 | Work for superuser creation page starts | | 2023-07-21| Script for generating Mathesar .deb file starts | | 2023-07-26 | Superuser creation page design specs will be completed| | 2023-07-28| Script for generating Mathesar .deb file is completed | | 2023-08-03 | Superuser creation page frontend work is completed and added to develop| | 2023-08-04| Work for Mathesar + Postgres docker image completed | | 2023-08-04| Few other pull requests for issues related to stretch goals will be merged into develop |
High-level view of implementation details¶
- Superuser creation page
- We will be using middleware to check for the non-existence of a superuser and redirect them to the superuser creation page which will be based on Django templates
- Debian package will be available as a systemmd service and will be created using dh-virtualenv. The script will build a python virtual environment for mathesar and will link to the system python. The implementation will closely follow Synapse deb file build script
- Mathesar + Postgres image will use our existing Mathesar docker image as a base and add PostgreSQL to the Mathesar + Postgres docker image
- Zipapps will be built using shiv
- SQLite codebase refactor is quite small as Mathesar uses a Postgres related field in only one place (for storing column order)
Github issue¶
Resources¶
- Project Approval Thread
- Project Update Thread
- Meeting notes: Parts I & II
- Meeting notes: Part III
- Meeting notes: Part IV
- Mukesh’s installation research (private)
References¶
Current steps¶
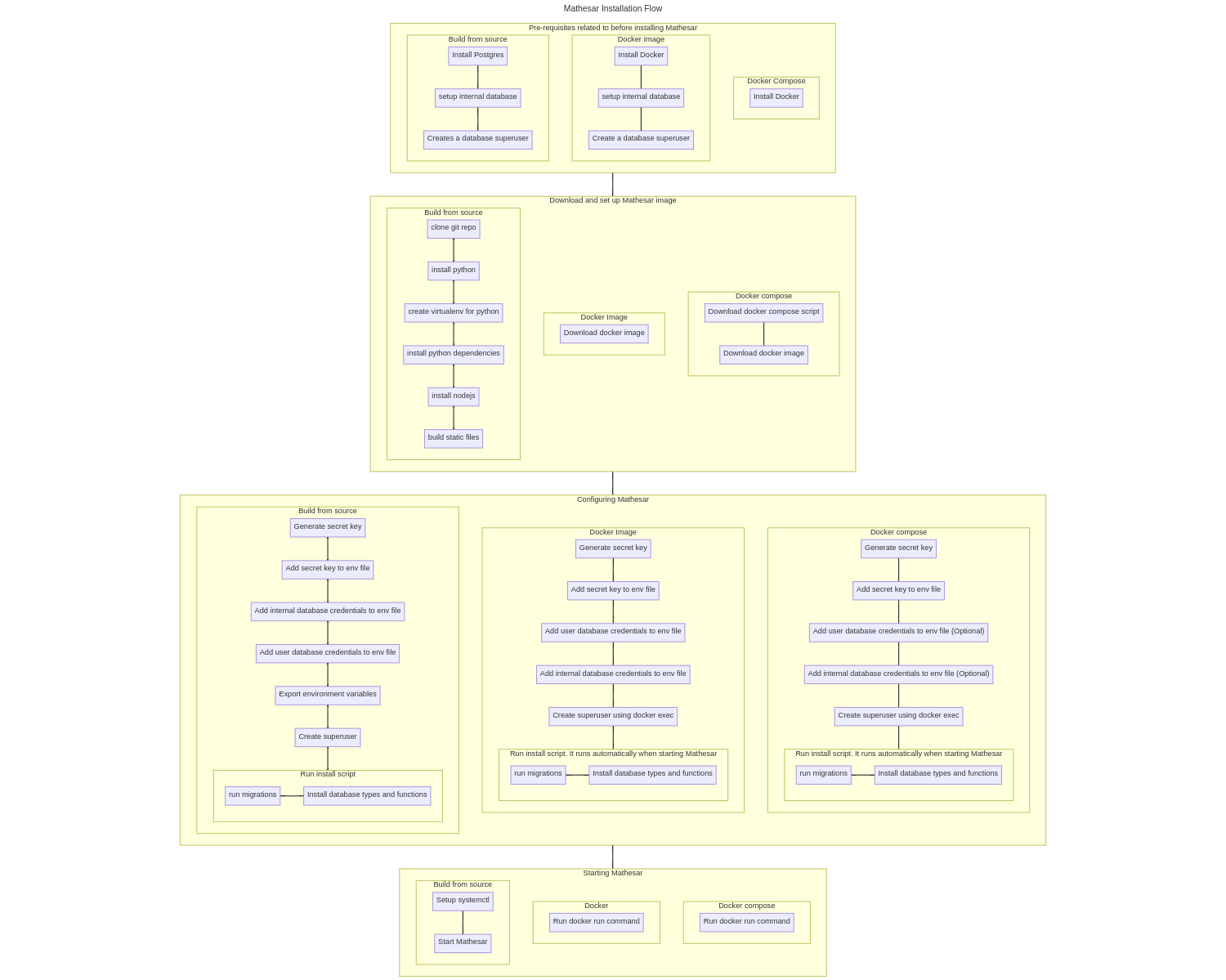 1. Pre-requisites before installing Mathesar
1. Pre-requisites before installing Mathesar
Docker Compose(1 step)
- Install Docker
</details>
<details>
<summary>Docker Image(3 steps)</summary>
- Install Docker
- Setup a database
- Create a database superuser
</details>
<details>
<summary>Building from source(3 steps)</summary>
- Install Postgres
- Setup mathesar database
- Create a database superuser
</details>
-
Downloading and set up Mathesar
Docker Compose(2 steps)
- Download docker compose script - Run docker compose command to downloadDocker Image(0 steps)
Building from source(6 steps)
- Clone git repo - Install python - Create virtualenv for python - Install python dependencies - Install nodejs - Build static files -
Configuring Mathesar
Docker Compose(6 steps)
- Generate secret key - Add secret key to env file - Add internal database credentials to env file - Add user database credentials to env file - Create superuser - Run install script(migrations and install database types)Mathesar docker Image(6 steps)
- Generate secret key - Add secret key to env file - Add internal database credentials to env file - Add user database credentials to env file - Create superuser - Run install script(migrations and install database types)Building from source(7 steps)
- Add internal database credentials to env file - Add user database credentials to env file - Generate secret key - Add secret key to env file - Export environment variables - Create superuser - Run install script(migrations and install database types) -
Starting Mathesar
Docker Compose(1 step)
- Run docker commandDocker Image(1 step)
- Run docker commandBuilding from source(2 steps)
- Create gunicorn systemctl script - Run the script
Expected steps after this project¶
1. Pre-requisites before installing Mathesar
Docker Compose(1 step)
- Install Docker
</details>
<details>
<summary>Mathesar docker Image(3 steps)</summary>
- Install Docker
- Setup a database
- Create a database superuser
</details>
<details>
<summary>Mathesar + Postgres docker Image(1 step)</summary>
- Install Docker
</details>
<details>
<summary>Non-Docker install(3 steps)</summary>
- Install Postgres
- Setup mathesar database
- Create a database superuser
</details>
-
Downloading and set up Mathesar
Docker Compose(2 steps)
- Download docker compose script - Run docker compose command to downloadBoth Docker Image(0 steps)
Non Docker Install Debian(1 step)
- Run apt installNon-Docker Non-debian(1 step)
- Install Python - Download zipapps -
Configuring Mathesar
Docker Compose(5 steps)
- Generate secret key - Add secret key to env file - Add internal database credentials to env file - Add user database credentials to env file - Run install script(migrations and install database types)Mathesar docker Image(5 steps)
- Generate secret key - Add secret key to env file - Add internal database credentials to env file - Add user database credentials to env file - Run install script(migrations and install database types)Mathesar + PG docker Image(5 steps)
- Generate secret key - Add secret key to env file - Run install script(migrations and install database types)Non-Docker install (6 steps)
- Add internal database credentials to env file - Add user database credentials to env file - Generate secret key - Add secret key to env file - Export environment variables - Run install script(migrations and install database types) -
Starting Mathesar
Docker Compose(1 step)
- Run docker commandDocker Image(1 step)
- Run docker commandNon-Docker(1 step)
- Run the Mathesar executable
Overview diagram¶
This diagram gives a overview of current steps (problems), solutions, steps after this cycle (outcome) along with information on how the solutions affect the current steps and the outcome.